更智能地保留类型别名
在 TypeScript 中,使用类型别名能够给某个类型起个新名字。
倘若你定义了一些函数,并且它们全都使用了 string | number | boolean 类型,那么你就可以定义一个类型别名来避免重复。
ts
TypeScript 使用了一系列规则来推测是否该在显示类型时使用类型别名。 例如,有如下的代码。
ts
如果在 Visual Studio,Visual Studio Code 或者 TypeScript 演练场编辑器中把鼠标光标放在 x 上,我们就会看到信息面板中显示出了 BasicPrimitive 类型。
同样地,如果我们查看由该文件生成的声明文件(.d.ts),那么 TypeScript 会显示出 doStuff 的返回值类型为 BasicPrimitive 类型。
那么你猜一猜,如果返回值类型为 BasicPrimitive 或 undefined 时会发生什么?
ts
可以在TypeScript 4.1 演练场中查看结果。
虽然我们希望 TypeScript 将 doStuff 的返回值类型显示为 BasicPrimitive | undefined,但是它却显示成了 string | number | boolean | undefined 类型!
这是怎么回事?
这与 TypeScript 内部的类型表示方式有关。
当基于一个联合类型来创建另一个联合类型时,TypeScript 会将类型标准化,也就是把类型展开为一个新的联合类型 - 但这么做也可能会丢失信息。
类型检查器不得不根据 string | number | boolean | undefined 类型来尝试每一种可能的组合并查看使用了哪些类型别名,即便这样也可能会有多个类型别名指向 string | number | boolean 类型。
TypeScript 4.2 的内部实现更加智能了。 我们会记录类型是如何被构造的,会记录它们原本的编写方式和之后的构造方式。 我们同样会记录和区分不同的类型别名!
有能力根据类型使用的方式来回显这个类型就意味着,对于 TypeScript 用户来讲能够避免显示很长的类型;同时也意味着会生成更友好的 .d.ts 声明文件、错误消息和编辑器内显示的类型及签名帮助信息。
这会让 TypeScript 对于初学者来讲更友好一些。
更多详情,请参考PR:改进保留类型别名的联合,以及PR:保留间接的类型别名。
元组类型中前导的/中间的剩余元素
在 TypeScript 中,元组类型用于表示固定长度和元素类型的数组。
ts
随着时间的推移,TypeScript 中的元组类型变得越来越复杂,因为它们也被用来表示像 JavaScript 中的参数列表类型。 结果就是,它可能包含可选元素和剩余元素,以及用于工具和提高可读性的标签。
ts
在 TypeScript 4.2 中,剩余元素会按它们的使用方式进行展开。
在之前的版本中,TypeScript 只允许 ...rest 元素位于元组的末尾。
但现在,剩余元素可以出现在元组中的任意位置 - 但有一点限制。
ts
唯一的限制是,剩余元素之后不能出现可选元素或其它剩余元素。 换句话说,一个元组中只允许有一个剩余元素,并且剩余元素之后不能有可选元素。
tsTryinterfaceClown {/*...*/}interfaceJoker {/*...*/}letA rest element cannot follow another rest element.1265A rest element cannot follow another rest element.StealersWheel : [...Clown [], 'me', ...Joker []];// ~~~~~~~~~~ 错误letAn optional element cannot follow a rest element.1266An optional element cannot follow a rest element.StringsAndMaybeBoolean : [...string[], boolean?];// ~~~~~~~~ 错误
这些不在结尾的剩余元素能够用来描述,可接收任意数量的前导参数加上固定数量的结尾参数的函数。
ts
尽管 JavaScript 中没有声明前导剩余参数的语法,但我们仍可以将 doStuff 函数的参数声明为带有前导剩余元素 ...args 的元组类型。
使用这种方式可以帮助我们描述许多的 JavaScript 代码!
更多详情,请参考 PR。
更严格的 in 运算符检查
在 JavaScript 中,如果 in 运算符的右操作数是非对象类型,那么会产生运行时错误。
TypeScript 4.2 确保了该错误能够在编译时被捕获。
tsTry'foo' inType 'number' is not assignable to type 'object'.2322Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'object'.42 ;// The right-hand side of an 'in' expression must not be a primitive.
这个检查在大多数情况下是相当保守的,如果你看到提示了这个错误,那么代码中很可能真的有问题。
非常感谢外部贡献者 Jonas Hübotter 的 PR!
--noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature
在 TypeScript 刚开始支持索引签名时,它只允许使用方括号语法来访问索引签名中定义的元素,例如 person["name"]。
ts
这就导致了在处理带有任意属性的对象时变得烦锁。
例如,假设有一个容易出现拼写错误的 API,容易出现在属性名的末尾位置多写一个字母 s 的错误。
ts
为了便于处理以上情况,在从前的时候,TypeScript 允许使用点语法来访问通过字符串索引签名定义的属性。 这会让从 JavaScript 代码到 TypeScript 代码的迁移工作变得容易。
然而,放宽限制同样意味着更容易出现属性名拼写错误。
ts
在某些情况下,用户会想要选择使用索引签名 - 在使用点号语法进行属性访问时,如果访问了没有明确定义的属性,就得到一个错误。
这就是为什么 TypeScript 引入了一个新的 --noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature 编译选项。
在该模式下,你可以有选择的启用 TypeScript 之前的行为,即在上述使用场景中产生错误。
该编译选项不属于 strict 编译选项集合的一员,因为我们知道该功能只适用于部分用户。
更多详情,请参考 PR。 我们同时要感谢 Wenlu Wang 为该功能的付出!
abstract 构造签名
TypeScript 允许将一个类标记为 abstract。 这相当于告诉 TypeScript 这个类只是用于继承,并且有些成员需要在子类中实现,以便能够真正地创建出实例。
tsTryabstract classShape {abstractgetArea (): number;}// 不能创建抽象类的实例newCannot create an instance of an abstract class.2511Cannot create an instance of an abstract class.Shape ();classSquare extendsShape {#sideLength: number;constructor(sideLength : number) {super();this.#sideLength =sideLength ;}getArea () {return this.#sideLength ** 2;}}// 没问题newSquare (42);
为了能够确保一贯的对 new 一个 abstract 类进行限制,不允许将 abstract 类赋值给接收构造签名的值。
tsTryabstract classShape {abstractgetArea (): number;}interfaceHasArea {getArea (): number;}// 不能将抽象构造函数类型赋值给非抽象构造函数类型。letType 'typeof Shape' is not assignable to type 'new () => HasArea'. Cannot assign an abstract constructor type to a non-abstract constructor type.2322Type 'typeof Shape' is not assignable to type 'new () => HasArea'. Cannot assign an abstract constructor type to a non-abstract constructor type.: new () => Ctor HasArea =Shape ;
如果有代码调用了 new Ctor,那么上述的行为是正确的,但若想要编写 Ctor 的子类,就会出现过度限制的情况。
ts
对于内置的工具类型InstanceType来讲,它也不是工作得很好。
ts
这就是为什么 TypeScript 4.2 允许在构造签名上指定 abstract 修饰符。
ts
在构造签名上添加 abstract 修饰符表示可以传入一个 abstract 构造函数。
它不会阻止你传入其它具体的类/构造函数 - 它只是想表达不会直接调用这个构造函数,因此可以安全地传入任意一种类类型。
这个特性允许我们编写支持抽象类的混入工厂函数。
例如,在下例中,我们可以同时使用混入函数 withStyles 和 abstract 类 SuperClass。
ts
注意,withStyles 展示了一个特殊的规则,若一个类(StyledClass)继承了被抽象构造函数所约束的泛型值,那么这个类也需要被声明为 abstract。
由于无法知道传入的类是否拥有更多的抽象成员,因此也无法知道子类是否实现了所有的抽象成员。
更多详情,请参考 PR。
使用 --explainFiles 来理解工程的结构
TypeScript 用户时常会问“为什么 TypeScript 包含了这个文件?”。
推断程序中所包含的文件是个很复杂的过程,比如有很多原因会导致使用了 lib.d.ts 文件的组合,会导致 node_modules 中的文件被包含进来,会导致有些已经 exclude 的文件被包含进来。
这就是 TypeScript 提供 --explainFiles 的原因。
sh
在使用了该选项时,TypeScript 编译器会输出非常详细的信息来说明某个文件被包含进工程的原因。 为了更易理解,我们可以把输出结果存到文件里,或者通过管道使用其它命令来查看它。
sh
通常,输出结果首先会给列出包含 lib.d.ts 文件的原因,然后是本地文件,再然后是 node_modules 文件。
目前,TypeScript 不保证输出文件的格式 - 它在将来可能会改变。 关于这一点,我们也打算改进输出文件格式,请给出你的建议!
更多详情,请参考 PR!
改进逻辑表达式中的未被调用函数检查
感谢 Alex Tarasyuk 提供的持续改进,TypeScript 中的未调用函数检查现在也作用于 && 和 || 表达式。
在 --strictNullChecks 模式下,下面的代码会产生错误。
ts
更多详情,请参考 PR。
解构出来的变量可以被明确地标记为未使用的
感谢 Alex Tarasyuk 提供的另一个 PR,你可以使用下划线(_ 字符)将解构变量标记为未使用的。
ts
在之前,如果 _first 未被使用,那么在启用了 noUnusedLocals 时 TypeScript 会产生一个错误。
现在,TypeScript 会识别出使用了下划线的 _first 变量是有意的未使用的变量。
更多详情,请参考 PR。
放宽了在可选属性和字符串索引签名间的限制
字符串索引签名可用于为类似于字典的对象添加类型,它表示允许使用任意的键来访问对象:
ts
当然了,对于不在字典中的电影名而言 movieWatchCount[title] 的值为 undefined。(TypeScript 4.1 增加了 --noUncheckedIndexedAccess 选项,在访问索引签名时会增加 undefined 值。)
即便一定会有 movieWatchCount 中不存在的属性,但在之前的版本中,由于 undefined 值的存在,TypeScript 会将可选对象属性视为不可以赋值给兼容的索引签名。
ts
TypeScript 4.2 允许这样赋值。
但是不允许使用带有 undefined 类型的非可选属性进行赋值,也不允许将 undefined 值直接赋值给某个属性:
ts
这条新规则不适用于数字索引签名,因为它们被当成是类数组的并且是稠密的:
ts
更多详情,请参考 PR。
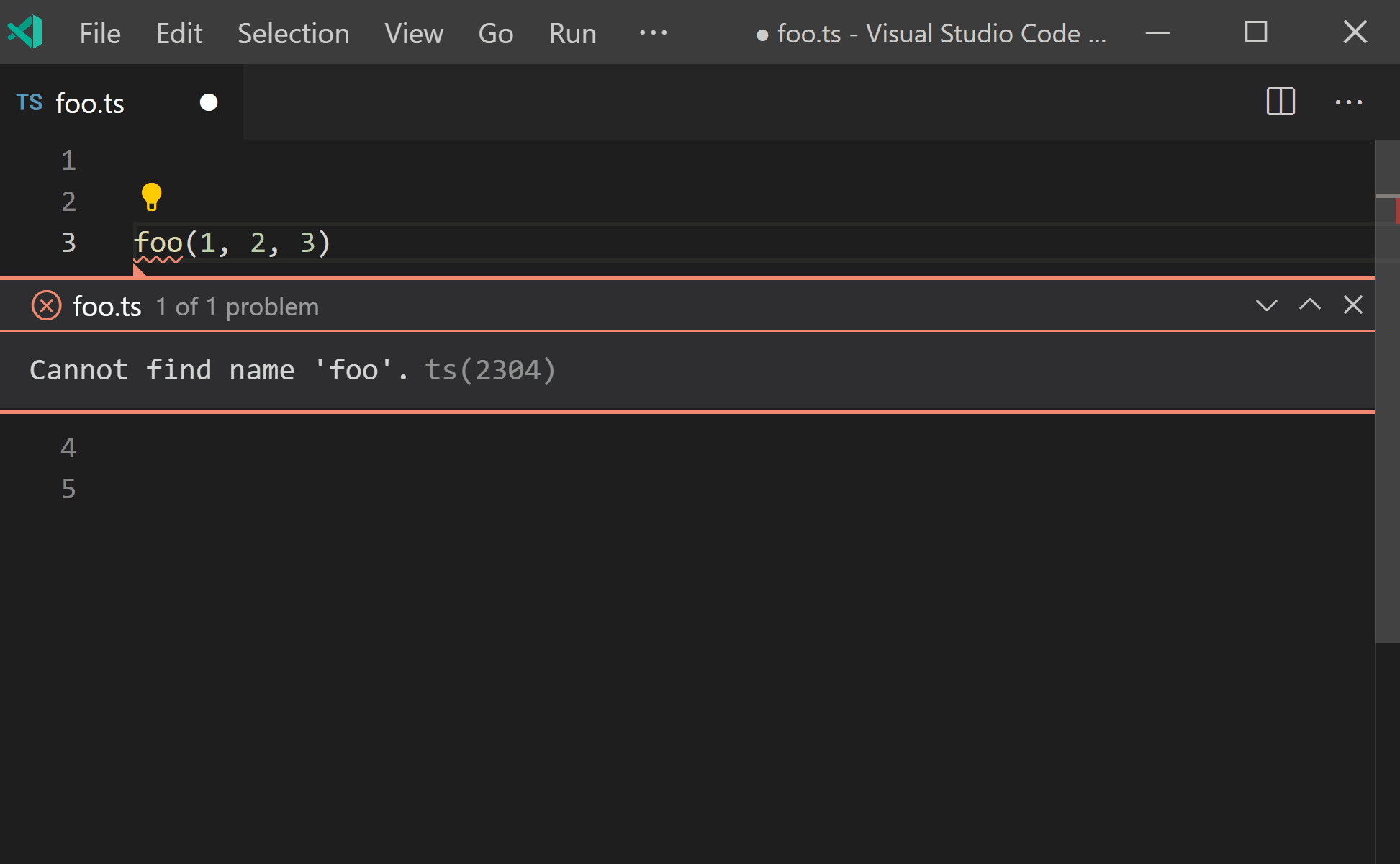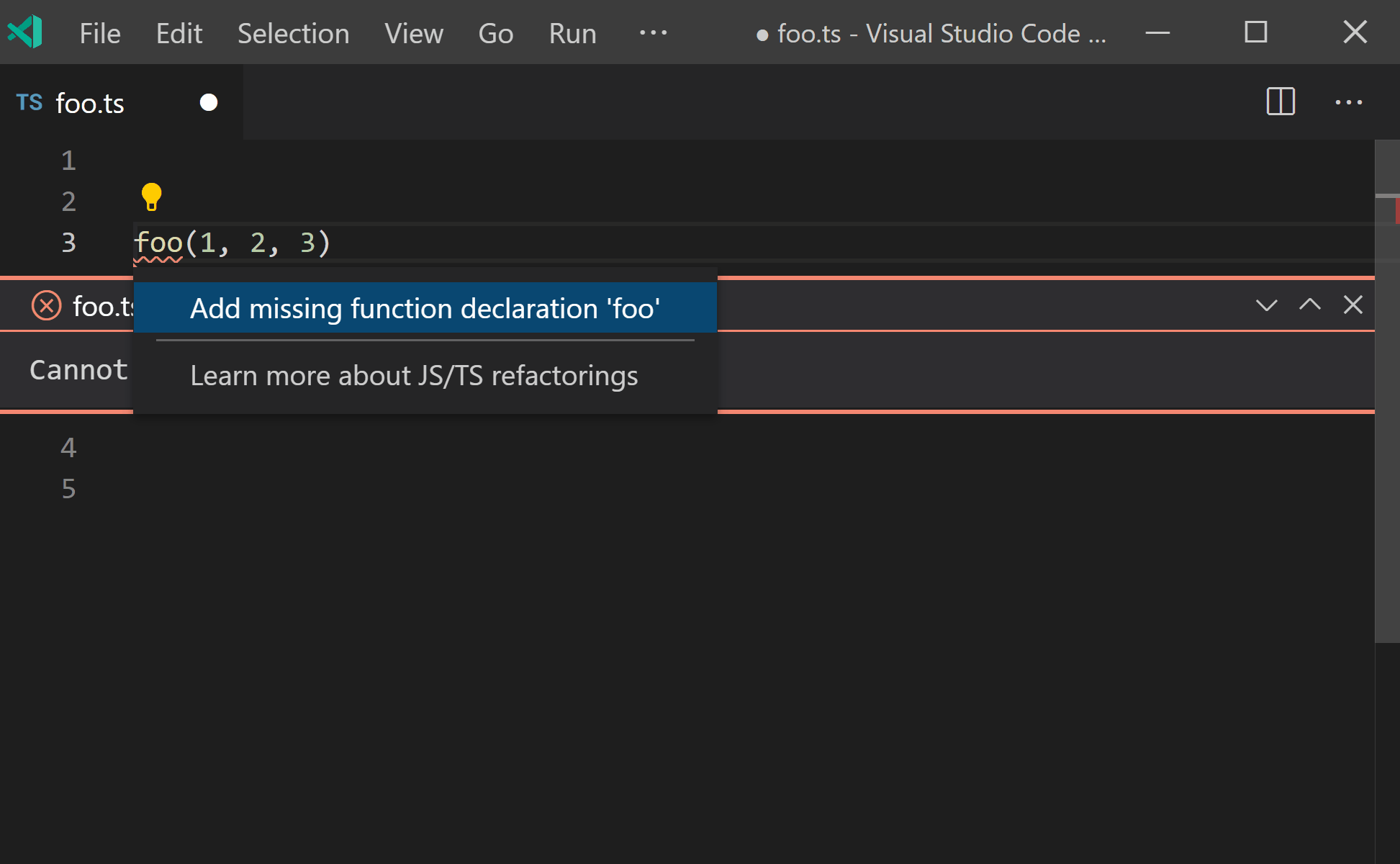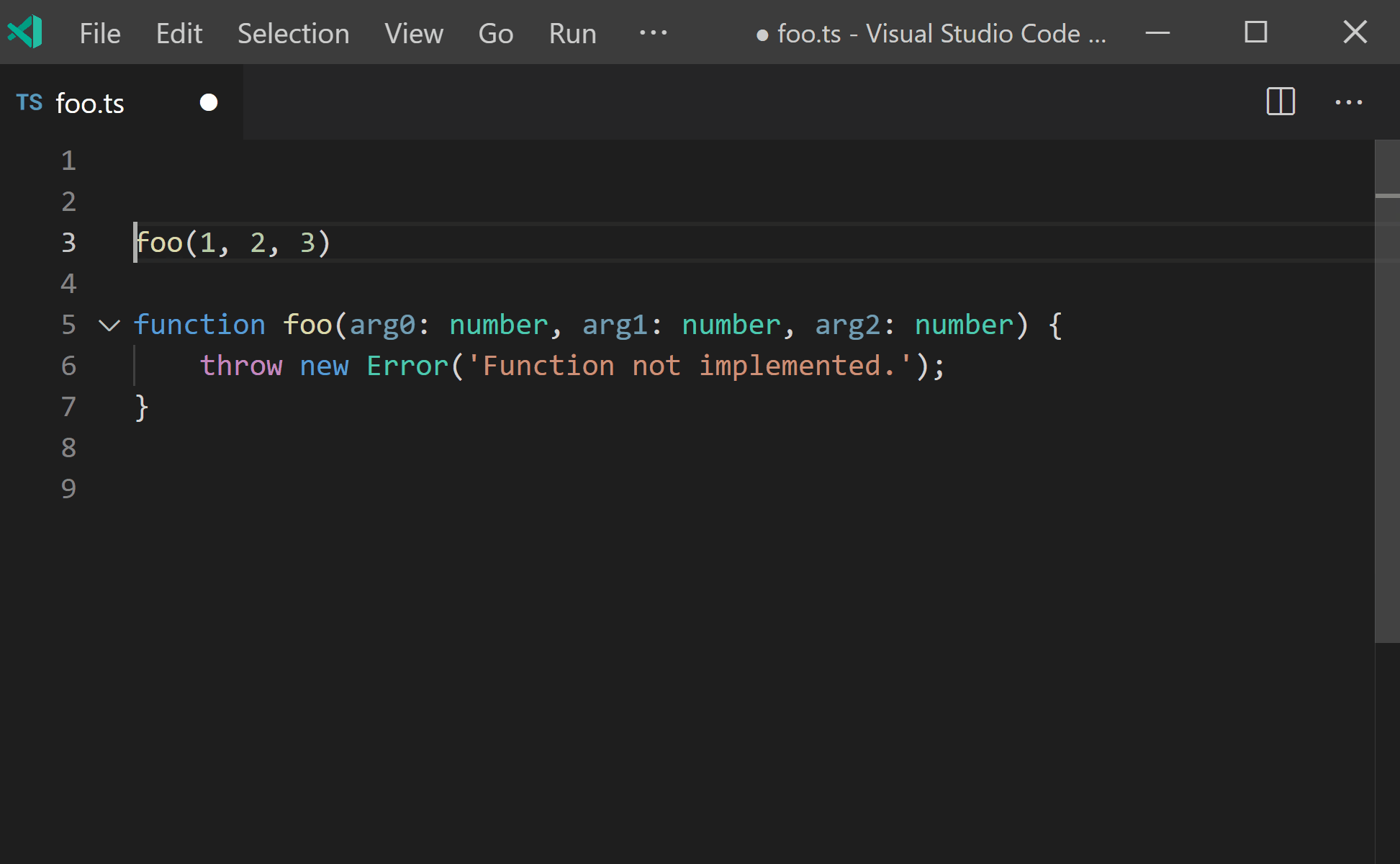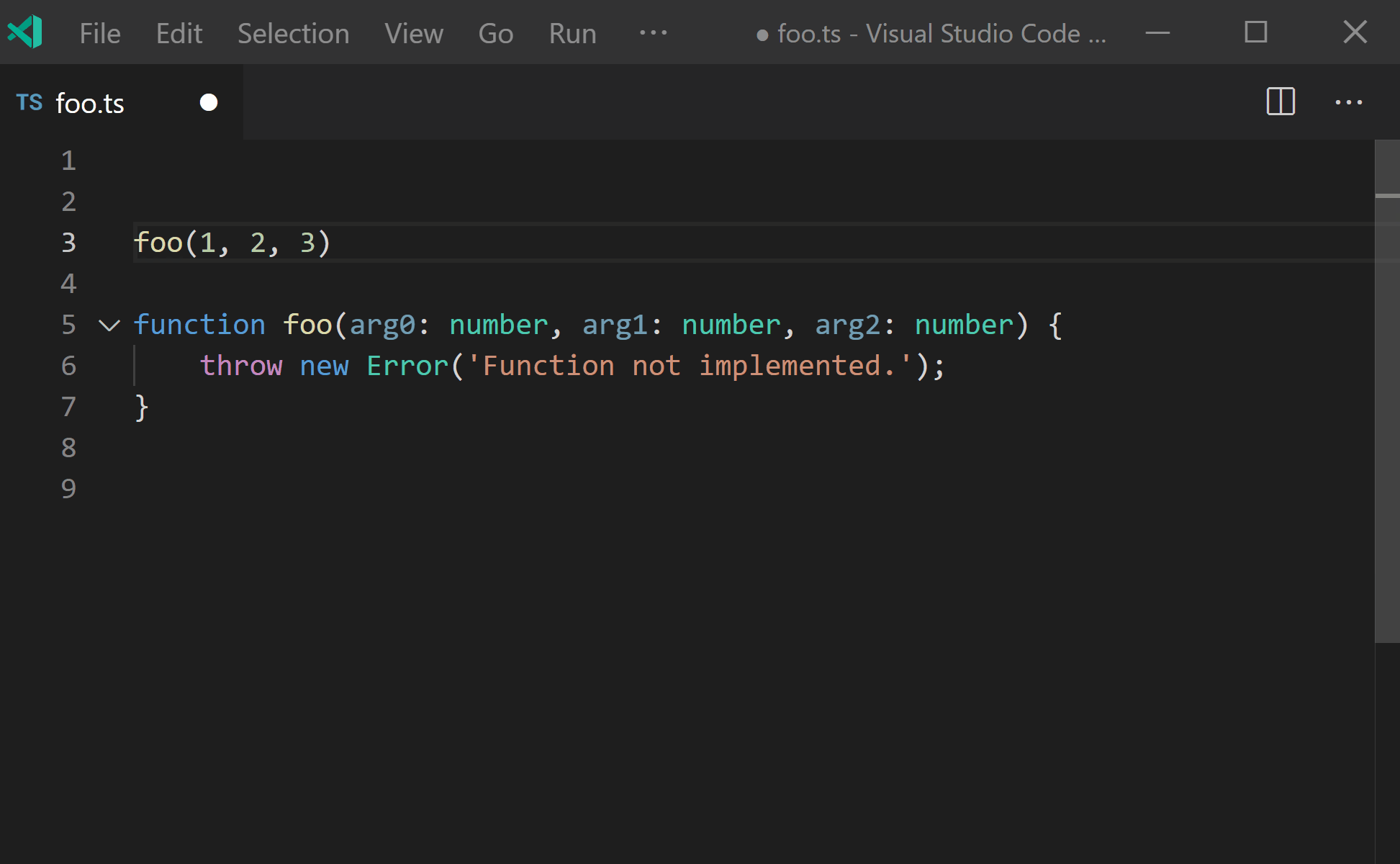
声明缺失的函数
感谢 Alexander Tarasyuk 提交的 PR,TypeScript 支持了一个新的快速修复功能,那就是根据调用方来生成新的函数和方法声明!